
Introduction:-
In modern cloud computing environments, deploying and managing serverless applications is becoming increasingly prevalent due to its scalability and cost-effectiveness. #AWS CloudFormation, a service offered by #Amazon Web Services (AWS), empowers users to define and provision infrastructure resources in a structured and repeatable manner. One essential component of serverless applications is #Lambda layers, which allow code and libraries to be shared across multiple #Lambda functions, promoting code reuse and maintainability.
#AWS CloudFormation template written in #YAML format. CloudFormation is a service provided by #AWS that allows you to define and provision infrastructure resources in a declarative manner. This template is specifically designed to create an #AWS Lambda layer. Let me break down the key sections and components of this template:
#AWSTemplateFormatVersion: Specifies the CloudFormation template version being used.
Transform: Specifies that the template uses the AWS Serverless Application Model (AWS SAM) for defining #serverless resources.
Description: A brief description of the #CloudFormation template.
Parameters: This section defines the input parameters that users can provide when deploying the stack. These parameters allow customization of the deployment.
EnvironmentName: A string parameter for specifying the environment name (e.g., "dev" or "production").LambdaLayerName: A string parameter for specifying the name of the Lambda layer.CodeS3Bucket: A string parameter for specifying the S3 bucket where the #Lambda artifact is stored.CodeS3Key: A string parameter for specifying the #S3 key for the #Lambda artifact.
5. Mappings and Conditions: These sections are currently empty and can be used for more advanced configuration if needed.
6. Resources: This section defines the #AWS resources to be created. In this case, it creates an #AWS Lambda layer named BaseLine14xLambdaLayer. Key properties of this resource include:
Type: Specifies the resource type asAWS::Lambda::LayerVersion.CompatibleRuntimes: Specifies the runtime compatibility for the Lambda layer (nodejs14.x in this case).Content: Specifies the #S3 bucket and key where the Lambda layer content (code) is located.Description: Describes the #Lambda layer with a combination of theEnvironmentNameandLambdaLayerName.LayerName: Specifies the name of the #Lambda layer.LicenseInfo: Specifies the license information for the layer (MIT in this case).
7. Outputs: This section defines the stack outputs, which are values that can be used after the stack is deployed. It exports the ARN of the #Lambda layer as an output with a name derived from the EnvironmentName and LambdaLayerName parameters.
Users can deploy this #CloudFormation template by providing values for the specified parameters, and it will create the specified #AWS Lambda layer with the specified configuration.
Deployment Steps
Follow these steps to upload and create the #CloudFormation stack using the #AWS Management Console:
- Sign in to the #AWS Management Console: Log in to your AWS account if you haven’t already.
2. Navigate to #CloudFormation: Go to the #AWS CloudFormation service from the #AWS Management Console.
3. Click the “Create stack” button.
4. Upload the CloudFormation template file (YAML).
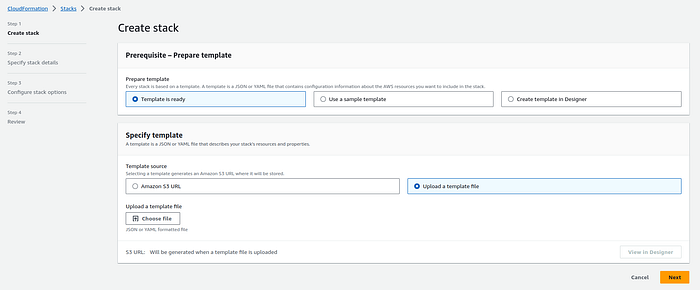
Yaml file :
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Description: Lambda layer
Parameters:
EnvironmentName:
Description: Environment name for the application
Type: String
ConstraintDescription: Specify either dev or production
LambdaLayerName:
Description: Application Name
Type: String
CodeS3Bucket:
Description: S3 Bucket in which the artifacts are stored
Type: String
MinLength: 3
CodeS3Key:
Description: S3 Key for the lambda artifact
Type: String
MinLength: 3
Mappings: {}
Conditions: {}
Resources:
BaseLine14xLambdaLayer:
Type: AWS::Lambda::LayerVersion
Properties:
CompatibleRuntimes:
- nodejs14.x
Content:
S3Bucket: !Ref CodeS3Bucket
S3Key: !Ref CodeS3Key
Description: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-${LambdaLayerName}
LayerName: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-${LambdaLayerName}
LicenseInfo: MIT
Outputs:
BaseLine14xLambdaLayerArn:
Description: Lambda layer arn.
Value: !Ref BaseLine14xLambdaLayer
Export:
Name: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-${LambdaLayerName}-arn'
5. Specify Stack Details:
Enter a Stack name for your deployment.
Provide parameter values as needed.
Review and acknowledge the capabilities .
You can set additional stack options or tags if necessary.
6. Review and Create:
Review the stack details and configuration.
Click “Create stack” to initiate the deployment.
7. Monitor Stack Creation:
The CloudFormation stack creation process will begin.
Monitor the stack events in the AWS Management Console.
Conclusion
AWS #CloudFormation template serves as a valuable tool for streamlining the creation and management of #Lambda layers in #AWS serverless applications. By offering a structured and parameterized approach, it allows users to customize the #Lambda layer’s environment name, name, and associated #S3 artifacts. This template promotes best practices in serverless development by enabling code reuse and separation of concerns, ultimately leading to more maintainable and efficient serverless applications.
