Cloud Watch dashboard for monitoring EC2 instance using Terragrunt.

OverView :-
#CloudWatch dashboards provide a centralized and customizable view of your #EC2 metrics, such as CPU utilization, network traffic, disk I/O, and more. By creating a dedicated dashboard, you can monitor the health and performance of your EC2 instances at a glance, enabling you to make informed decisions and take proactive actions to optimize resource utilization and maintain application stability.
Pre-Requestisites:-
An AWS account with appropriate permissions to create CloudWatch dashboards.
#Terraform & #Terragrunt installed on your local machine.
#AWS credentials properly configured.
Step 1:- Open an virtual editor (vs code) for developing the code.
Step 2:- For creating cloud watch dashboard using terragrunt, Create a directory named cloud-watch-dashboard in your home directory. In that cloud-watch-dashboard directory create a one-more folder with name (module)and create two files called main.tf and variable.tf in the module Folder.
step 3:- Open the main.tf file and paste the below code to create a cloud watch dashboard.
resource "aws_cloudwatch_dashboard" "main" {
dashboard_name = var.dashboard_name
dashboard_body = <<EOF
{
"widgets" : [
{
"type": "metric",
"x": 0,
"y": 0,
"width": 12,
"height": 6,
"properties": {
"metrics": [
["AWS/EC2",
"CPUUtilization",
"InstanceId",
"${var.instance_id}"
]
],
"period": 300,
"stat": "Average",
"region": "${var.region}",
"title": "EC2 Instance CPU"
}
},
{
"type": "metric",
"x": 0,
"y": 10,
"width": 12,
"height": 6,
"properties": {
"metrics": [
["AWS/EC2", "NetworkIn",
"InstanceId",
"${var.instance_id}"
]
],
"period": 300,
"stat": "Average",
"region": "${var.region}",
"title": "EC2 Instance Network In"
}
},
{
"type": "metric",
"x": 0,
"y": 16,
"width": 12,
"height": 6,
"properties": {
"metrics": [
["AWS/EC2",
"NetworkOut",
"InstanceId",
"${var.instance_id}"
]
],
"period": 300,
"stat": "Average",
"region": "${var.region}",
"title": "EC2 Instance Network Out"
}
},
{
"type": "metric",
"x": 0,
"y": 22,
"width": 12,
"height": 6,
"properties": {
"metrics": [
["AWS/EC2",
"DiskReadBytes",
"InstanceId",
"${var.instance_id}"],
["AWS/EC2",
"DiskWriteBytes",
"InstanceId",
"${var.instance_id}"
]
],
"period": 300,
"stat": "Average",
"region": "${var.region}",
"title": "EC2 Instance Disk IO"
}
}
]
}
EOF
}
step 4: Define variables in variable.tf file for the above main.tf file.
variable "instance_id" {
type = string
description = "Id of the instance"
}
variable "dashboard_name" {
type = string
description = "Name of the Dashboard"
}
variable "region" {
type = string
description = "default region"
}
Step 5:- After setting up all those things in the module folder. create one folder named cloud-watch in the cloud-watch-dashboard directory, within that cloud-watch folder create a file called terragrunt.hcl
Step 6 :- Here, we are defining the variable values and deploying our code using terragrunt. u can use the below code to create the dashboard using terragrunt.
terraform {
source = "../Dashboard"
}
include "root" {
path = find_in_parent_folders()
}
locals {
instance_id = "i-jjb8967799756njbd"
region = "us-east-1"
}
inputs = {
dashboard_name = "ec2-cloud_watch-dashboard"
instance_id = local.instance_id
region = local.region
}
Step-7 :- After completed all those file setup.Open the terminal.
Step-8:- Locate to your cloud-watch folder which is being created in your module directory.(as shown in the below picture)
Step-9 :- In that location only you need to perform the command terragrunt init.
Step-10: After completion of the initialization. Next need to perform terragrunt plan.After successfully planed. Next need to perform terragrunt apply.
Step 11:- once it is applied. Login to your #AWS console.
Step 12: In your #AWS management console, Search for cloud watch service.
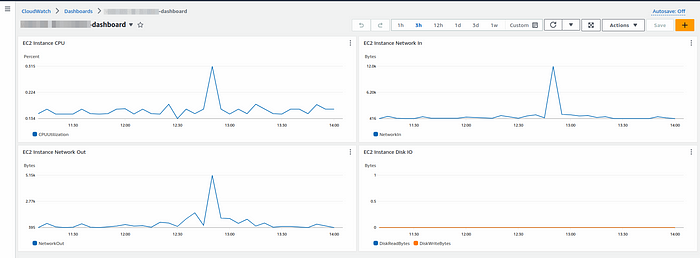
Step 13:- you can see the cloudwatch dashboard has been created.
Source-code link :- “github.com/MahiraTechnology/Mahira-medium.git***”***
Conclusion :-
CloudWatch dashboards provide a centralized view of your #AWS resources, allowing you to #monitor performance, #troubleshoot issues, and make informed decisions based on #real-time data. With #Terraform, you can define and manage your dashboards as code, enabling repeatability, #version control, and easy collaboration within your #infrastructure-as-code workflow.
