Empower Your Database Security: Creating a Postgres Read-Only User with Terraform

Introduction :-
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of creating a read-only user for a #PostgreSQL database using #Terraform. By following this step-by-step tutorial, you will be able to leverage Terraform’s #infrastructure-as-code capabilities to provision and manage your #PostgreSQL database resources, while ensuring the #security and access control of your data.
Prerequisites: To follow along with this tutorial, you will need the following:-
An AWS account with appropriate permissions to create resources like Ec2 Instances, RDS instances, and #Terraform access.
#Terraform installed on your local machine.
Basic knowledge of #PostgreSQL and #AWS RDS (Relational Database Service).
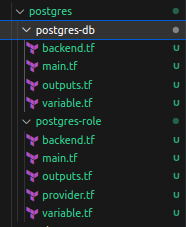
Step 1 :- Create a folder named postgres in your home directory and with in the postgres folder create two more folders with name postgres-db and postgres-role as shown below.
Step 2 :- Now create a RDS instance and Bastion-host instance within the postgre-db folder main.tf file using terraform.(Refer Below code)
resource "random_password" "db_master_password" {
length = 16
special = false
}
resource "random_password" "db_read_only_password" {
length = 16
special = false
}
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret" "postgres_db" {
name = var.secret_name
recovery_window_in_days = 0
}
resource "aws_secretsmanager_secret_version" "postgres_db" {
secret_id = aws_secretsmanager_secret.postgres_db.id
secret_string = <<EOT
{
"master_username": "${var.db_username}",
"master_password": "${random_password.db_master_password.result}",
"read_only_username": "${var.db_username}_db",
"read_only_password": "${random_password.db_read_only_password.result}",
}
EOT
}
resource "aws_vpc" "default" {
cidr_block = var.vpc_cidr_block
tags = {
Name = "${var.vpc_name}"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "public_subnet" {
count = var.count_index
vpc_id = aws_vpc.default.id
cidr_block = var.public_subnet_cidr_blocks[count.index]
availability_zone = var.azs[count.index]
tags = {
Name = "Public Subnet"
}
}
resource "aws_subnet" "db_subnet" {
count = var.count_index
vpc_id = aws_vpc.default.id
cidr_block = var.db_subnets_cidr_blocks[count.index]
availability_zone = var.azs[count.index] # Replace with your desired availability zone
tags = {
Name = "Database Subnets"
}
}
# Create Internet Gateway
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "igw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.default.id
tags = {
Name = "postgres IGW"
}
}
# Create Web layber route table
resource "aws_route_table" "web-rt" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.default.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.igw.id
}
tags = {
Name = "WebRT"
}
}
resource "aws_security_group" "allow_all" {
name = "sg_for_rds"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.default.id
description = "RDS instance security group"
ingress {
description = "All Traffic"
from_port = 5432
to_port = 5432
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = [var.public_subnet_cidr_blocks[0],
var.public_subnet_cidr_blocks[1],
var.public_subnet_cidr_blocks[2],
var.db_subnets_cidr_blocks[0],
var.db_subnets_cidr_blocks[1],
var.db_subnets_cidr_blocks[2]]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = "allow_all"
}
}
resource "aws_db_instance" "postgres_rds" {
allocated_storage = var.allocated_storage
identifier = var.identifier
storage_type = var.storage_type
engine = var.engine
engine_version = var.engine_version
instance_class = var.instance_class
db_name = var.db_name
username = var.db_username
password = random_password.db_read_only_password.result
parameter_group_name = var.parameter_group_name
db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.db-subnet.name
skip_final_snapshot = true
}
resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "db-subnet" {
name = var.db_subnet_group_name
subnet_ids = [
aws_subnet.db_subnet[0].id,
aws_subnet.db_subnet[1].id,
aws_subnet.db_subnet[2].id
]
}
data "http" "my_ip" {
url = "http://checkip.amazonaws.com/"
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "bastion_role" {
name = "bastion-role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Action = "sts:AssumeRole"
Effect = "Allow"
Sid = ""
Principal = {
Service = "ec2.amazonaws.com"
}
},
]
})
}
resource "aws_security_group" "sg-bastion-host" {
name = "sg_for_bastion-host"
description = "security group for bastion host"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.default.id
ingress {
description = "ssh"
from_port = 22
to_port = 22
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["${chomp(data.http.my_ip.body)}/32"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = "sg_for_bastion"
}
}
resource "aws_iam_instance_profile" "iam_profile" {
name = "bastion-profile"
role = aws_iam_role.bastion_role.name
}
resource "aws_instance" "bastion_host" {
ami = var.ami_id
instance_type = var.instance_type
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.sg-bastion-host.id]
key_name = aws_key_pair.bastion-key.key_name
iam_instance_profile = aws_iam_instance_profile.iam_profile.id
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public_subnet[0].id
tags = {
Name = "bastion-host"
}
}
resource "tls_private_key" "this" {
algorithm = "RSA"
}
resource "aws_key_pair" "bastion-key" {
key_name = var.key_name
public_key = tls_private_key.this.public_key_openssh
provisioner "local-exec" { # Create a "myKey.pem" to your computer!!
command = "echo '${tls_private_key.this.private_key_pem}' > ~/${var.key_name}.pem"
}
}
variable "identifier" {
default = "postgres-rds-db"
}
variable "allocated_storage" {
default = 20
}
variable "storage_type" {
default = "gp2"
}
variable "engine" {
default = "postgres"
}
variable "engine_version" {
default = 14.7
}
variable "instance_class" {
default = "db.t3.micro"
}
variable "db_name" {
default = "postgres_db"
}
variable "parameter_group_name" {
default = "default.postgres14"
}
variable "public_subnet_cidr_blocks" {
type = list(string)
default = ["10.50.0.0/24", "10.50.1.0/24", "10.50.2.0/24"]
}
variable "db_subnets_cidr_blocks" {
type = list(string)
default = ["10.50.16.0/24", "10.50.32.0/24", "10.50.64.0/24"]
}
variable "vpc_cidr_block" {
description = "CIDR block for VPC"
default = "10.50.0.0/16"
}
variable "vpc_name" {
description = "Name of the VPC"
default = "open-source_projects"
}
variable "azs" {
type = list(string)
default = ["us-east-1a", "us-east-1b", "us-east-1c"]
}
variable "count_index" {
type = number
default = 3
}
variable "db_subnet_group_name" {
type = string
default = "db-subnet-group"
}
variable "secret_name" {
type = string
default = "Open-source"
}
variable "key_name" {
type = string
default = "postgres-key"
}
variable "ami_id" {
type = string
default = "ami-06ca3ca175f37dd66"
}
variable "instance_type" {
type = string
default = "t2.micro"
}
variable "db_username" {
type = string
default = "read_only_user"
}
variable "subnet_count" {
type = number
default = 1
}
Step 3:- Deploy the above code to create a postgre-db.
Step 4:- Next create a main.tf and variable.tf , provider.tf files in the postgres-role directory to create a db-read-only-user using terraform
Step 5:- Refer the below code to Create the postgres user and role .
# main.tf
provider "postgresql" {
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = "5434"
database = "postgres"
username = "${var.db_username}"
password = "${var.db_master_password}"
sslmode = "require"
connect_timeout = 15
superuser = false
}
resource "postgresql_role" "readonly" {
name = "readonly"
}
resource postgresql_grant "readonly_public" {
database = "postgres"
role = postgresql_role.readonly.name
schema = "public"
object_type = "table"
privileges = ["SELECT"]
}
resource "postgresql_role" "readonly_user" {
name = "${var.db_username}-db-role"
password = "${var.db_read_only_password}"
login = true
roles = [postgresql_role.readonly.name]
}
# variables.tf
variable "db_username" {
type = string
default = "read_only_user"
}
variable "secret_name" {
type = string
default = "Open-source"
}
# Note:- Login to aws management console, then navigate to secrets manager service and find the Open-source secret. Retrieve the secret values in Open-source secret to copy the master_password & db_read_only_password.
variable "db_master_password" {
type = string
description = "The master pasword of the postgres-db"
default = "GJpdsI2IhnAaMWaZ"
}
variable "db_read_only_password" {
type = string
description = "read only password of the postgres-db"
default = "myn1JubEHNTeZ9ju"
}
# provider.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
postgresql = {
source = "cyrilgdn/postgresql"
version = "1.19.0"
}
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "5.8.0"
}
}
}
Step 6:- First we need to run the tunneling command to #deploy the above postgres read only user creation code. Tunneling command will looks like below.
Step 7 :- Replace the below command values with your postgres-db and instance values. After replacing the values Open a terminal window and run the command.
ssh -i <.pem> -f -N -L 5434:<db-endponit>:5432 ec2-user@<bastion-host-public ip> -v
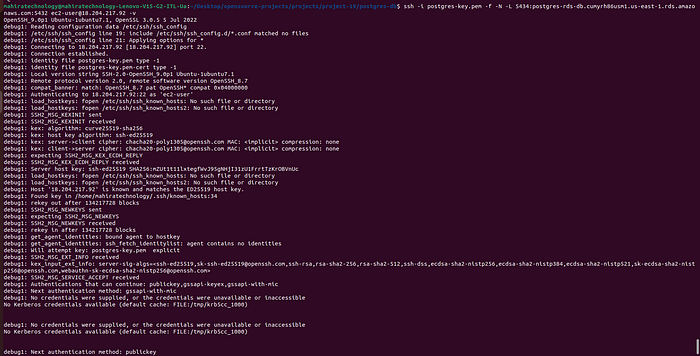
Step 8:- Keep the tunneling running on and open another terminal to deploy the postgres read only user code.
Step 9:- Once the code deploy’s successfully. Connect to your #pgadmin4 and check the user and role is being created or not. To connect to your pgadmin refer the below figure
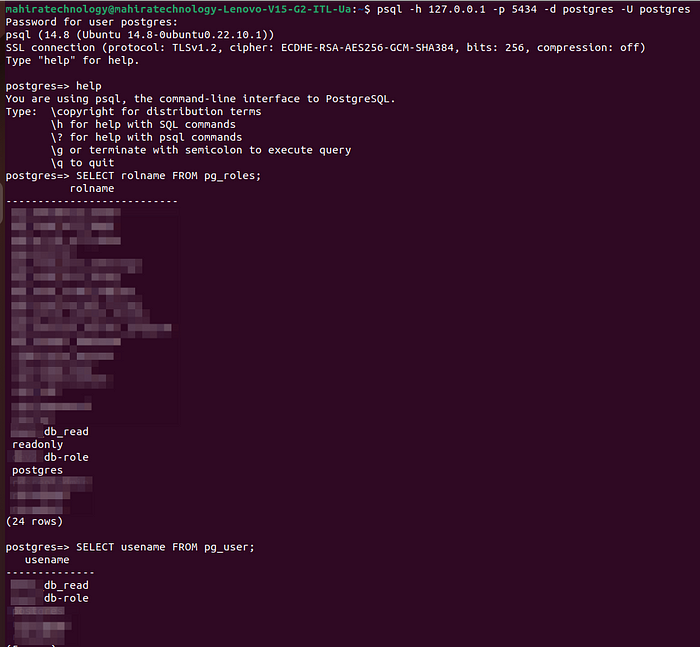
Step 9 :- As u can see the read-only-user and role is being created in postgres db (or) else u can verify by downloading the pgadmin4 and connecting to the db
Step 10 :- once u have connected with Desktop #PGadmin4. First register u r credentials in pgadmin4. as shown like below
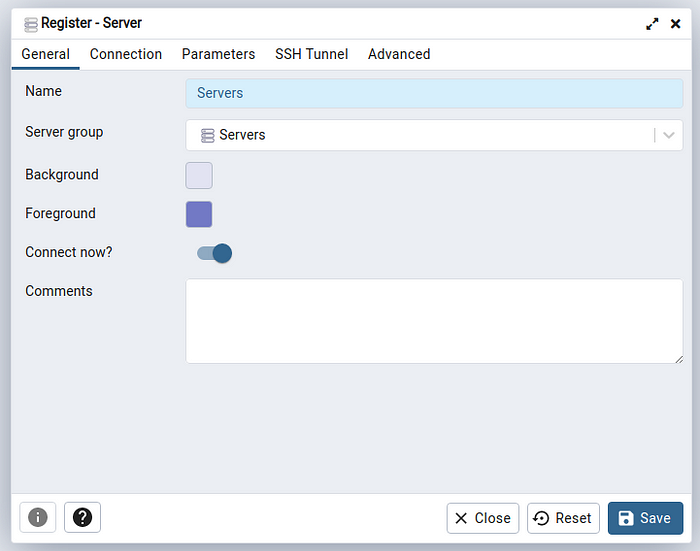
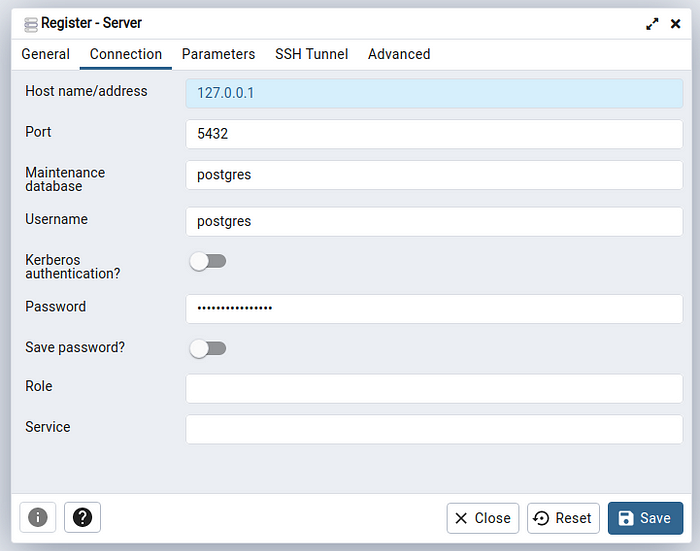
Step 11 :- after filling the db details, click on save to login to the #PgAdmin4.
Step 12 :- Once u registered the postgresdb. You are able to see the read-only-user in the postgresdb, as shown in below .
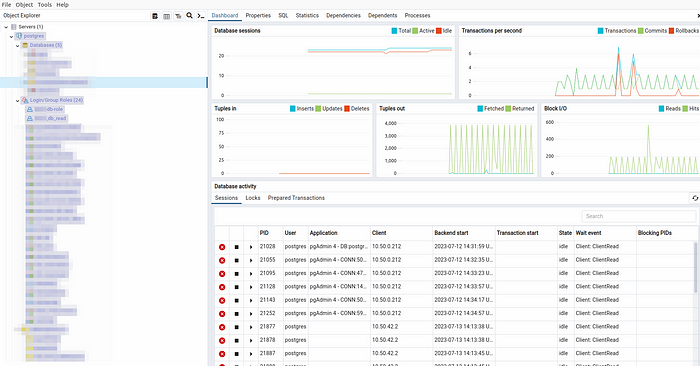
Conclusion :-
In this guide, we have demonstrated how to create a read-only user for a #PostgreSQL database using #Terraform. By following the step-by-step tutorial, users can leverage Terraform’s #infrastructure-as-code capabilities to provision and manage PostgreSQL database resources while ensuring data #security and access control.
The process involves creating an RDS instance, a bastion host, and the necessary security groups. Then, we use Terraform to create a read-only user, a role, and grant the necessary privileges to the user on the public schema of the PostgreSQL database.
By using #infrastructure as code, we can easily reproduce this setup across multiple environments with consistent configuration and #security. #Terraform allows us to version-control our infrastructure code, making it easier to track changes and #collaborate with a team.