Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Pipeline

Introduction:
#Continuous Integration and #Continuous Deployment (#CI/CD) has become a pivotal aspect of modern software development, streamlining the process from code changes to production deployment. In this context, the provided configuration file serves as a blueprint for a CI/CD pipeline designed to automate the build and #deployment of a #Node.js application. This configuration is a representation of a structured, automated workflow that ensures consistent, error-free deployments and can be seamlessly integrated into #CI/CD platforms and services.
Here’s a breakdown of the key sections and components in this configuration file:
- Version:
- The version of this pipeline configuration. In this case, it’s version 0.2.
2. Environment Variables:
The
envsection defines environment variables that are used within the pipeline.ENV,STACK, andSTACKTYPEare set to 'none' by default.There’s a reference to a secrets manager, which suggests that sensitive information (like the #GitHub token) is being managed securely.
3. Phases:
The pipeline is divided into several phases, each with specific commands to execute. The key phases are as follows:
install: This phase installs global and project-specific dependencies.
pre_build: This phase performs some checks and validations before the actual build.
build: This is where the application is built and configured based on environment and stack parameters.
post_build: This phase executes commands after the build is complete.
4. Install Phase:
It sets the #Node.js runtime version to 14.
Installs the latest version of npm globally.
Installs the #TypeScript globally.
Navigates to the “node-scripts” directory and installs project dependencies.
5. Pre_Build Phase:
- It performs conditional checks on the
STACKTYPEandSTACKenvironment variables. If they are not set properly, it fails the build with an exit code 1.
6. Build Phase:
It prints information about the build, including the environment, stack, and stack type.
Runs a build script using npm.
Executes a #Node.js script with specific stack and stack type parameters.
7. Post_Build Phase:
- This phase doesn’t have any failure conditions and simply prints “Build Complete.”
8. Artifacts:
Specifies that the artifacts generated during the build should be packaged into a zip file.
The
filessection specifies which files and directories should be included in the zip archive.base-directoryspecifies the base directory for the files to be included in the archive.
Deployment Steps
Follow these steps to upload and create the CloudFormation stack using the #AWS Management Console:
- Sign in to the #AWS Management Console: Log in to your AWS account if you haven’t already.
2. Navigate to CloudFormation: Go to the #AWS CloudFormation service from the AWS Management Console.
3. Click the “Create stack” button.
4. Upload the CloudFormation template file (YAML).
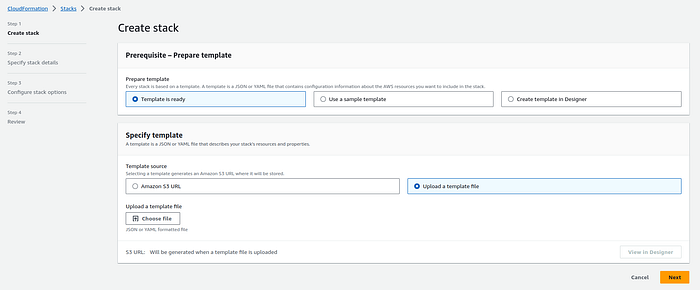
Yaml:
version: 2
jobs:
build:
docker:
- image: node:14 # Use an appropriate Node.js version
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2 # GitHub action for checking out code
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Build
run: npm run build
- name: Test
run: npm test
deploy:
needs: build
runs-on: ubuntu-latest # Use an appropriate runner
5. Specify Stack Details:
Enter a Stack name for your #deployment.
Provide parameter values as needed.
Review and acknowledge the capabilities .
You can set additional stack options or tags if necessary.
6. Review and Create:
Review the stack details and configuration.
Click “Create stack” to initiate the deployment.
7. Monitor Stack Creation:
The #CloudFormation stack creation process will begin.
#Monitor the stack events in the AWS Management Console.
Conclusion :-
The #CI/CD pipeline configuration presented here reflects a disciplined approach to #software deployment. It systematically handles the installation of dependencies, performs necessary checks, and #orchestrates the entire build process. It then packages the #artifacts and offers a clear post-build summary. Such pipelines are instrumental in reducing human error, improving collaboration, and #delivering code changes to users faster and with greater confidence.
By adhering to best practices in #CI/CD like this, #software development teams can significantly enhance their #development cycles, resulting in more agile and responsive systems, and ultimately, happier end-users.
