Demystifying AWS CloudFormation: Crafting an Amazon EKS Infrastructure

Introduction :-
The provided AWS CloudFormation template is a powerful tool for automating the deployment of an Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) cluster within the AWS cloud environment. EKS is a managed Kubernetes service that simplifies the process of running containerized applications at scale. This template streamlines the creation of the EKS cluster, along with essential IAM roles, security groups, and networking resources, allowing for secure and efficient Kubernetes deployments.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components and resources in your CloudFormation template:
- Parameters: These are inputs to your CloudFormation stack, allowing users to customize the deployment. Parameters include the environment name, EKS cluster name, network stack name, EFS port, GRPC port, and availability zone name.
2. Resources: These are the AWS resources that will be created and managed by your CloudFormation stack. Key resources include IAM roles for the EKS cluster and pods, security groups for EKS and EFS, the EKS cluster itself, and an EKS profile.
3. Outputs: These are values or references to resources that you want to make available to other CloudFormation stacks or services. In this case, you’re exporting the EKS OIDC connection URL and the EKS Pod Security Group.
4. IAM Roles: You’re creating two IAM roles, one for the EKS cluster itself (EKSIAMRole) and one for the pods (EKSpodexecutionRole). These roles define what actions the EKS cluster and pods can perform within AWS.
5. Security Groups: You’ve defined security groups for cluster communication with worker nodes (ControlPlaneSecurityGroup), security for Temporal Pods (PodSecurityGroup), and security for the Elastic File System (EFS) (EFSSecurityGroup). These security groups control inbound and outbound traffic for the associated resources.
6. EKS Cluster: The EKS cluster (EKSCluster) is created with the specified configuration, including the cluster name, IAM role, VPC configuration, and Kubernetes version.
7. EKS Profile: An EKS profile (EKSProfiles) is created, which associates the EKS cluster with a pod execution role, namespaces, and subnets. This profile defines which pods can run on the EKS cluster.
8. EFS Security Group: A security group (EFSSecurityGroup) for the Elastic File System (EFS) is defined, allowing inbound traffic from specific subnets.
9. Outputs: You’re exporting the EKS cluster endpoint URL and the EKS Pod Security Group so that they can be used in other CloudFormation stacks or services.
Overall, this template is designed to create and configure an EKS cluster with the necessary IAM roles, security groups, and networking settings to run Kubernetes workloads securely. Make sure to provide the required parameter values when launching this CloudFormation stack, and it should create the specified resources as per your configuration.
Deployment Steps -
Follow these steps to upload and create the CloudFormation stack using the AWS Management Console:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console: Log in to your AWS account if you haven’t already.
2. Navigate to CloudFormation: Go to the AWS CloudFormation service from the AWS Management Console.
3. Click the “Create stack” button.
4. Upload the CloudFormation template file (YAML).
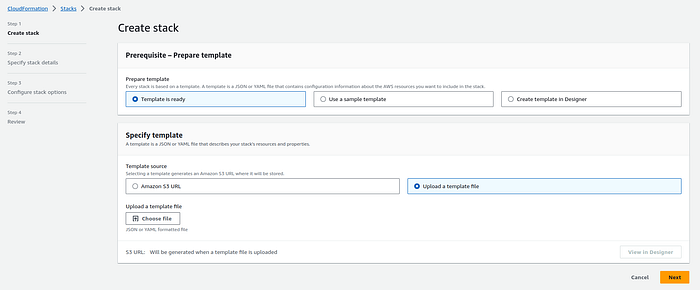
Yaml file :
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: "AWS CloudFormation Template for the EKS Cluster."
Parameters:
EnvironmentName:
Description: Environment name for the application
EKSClusterName:
Type: String
Description: The Desired name of your AWS EKS Cluster.
NetworkStackName:
Description: Name of an active CloudFormation stack of networking resources
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: "^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$"
EFSPort:
Description: EFS port
Default: '2049'
Type: Number
GRPCPort:
Description: GRPC port
Default: '7233'
Type: Number
AvailabilityZoneName:
Description: AvailabilityZone for EFS Filesystem
Default: ca-central-1a
Type: String
Resources:
EKSIAMRole:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
RoleName: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-${EKSClusterName}-iamrole'
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- eks.amazonaws.com
Action:
- 'sts:AssumeRole'
ManagedPolicyArns:
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSClusterPolicy
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSServicePolicy
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSVPCResourceController
EKSpodexecutionRole:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'
Properties:
RoleName: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-${EKSClusterName}-podexecrole'
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- eks-pods.amazonaws.com
Action:
- 'sts:AssumeRole'
EKSpodexecutionPolicy:
Type: 'AWS::IAM::Policy'
Properties:
PolicyName: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-${EKSClusterName}-podexecpolicy'
PolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- 'ecr:GetAuthorizationToken'
- 'ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability'
- 'ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer'
- 'ecr:BatchGetImage'
- 'logs:CreateLogStream'
- 'logs:CreateLogGroup'
- 'logs:DescribeLogStreams'
- 'logs:PutLogEvents'
Resource: '*'
Roles:
- !Ref EKSpodexecutionRole
ControlPlaneSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: Cluster communication with worker nodes
VpcId:
!ImportValue
'Fn::Sub': '${NetworkStackName}-VpcId'
PodSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: Security group for Temporal Pods
VpcId:
!ImportValue
'Fn::Sub': '${NetworkStackName}-VpcId'
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: !Ref GRPCPort
ToPort: !Ref GRPCPort
CidrIp:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet1Cidr
Description: !Sub Inbound from Private Subnet1 to ${EnvironmentName} GRPC Port
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: !Ref GRPCPort
ToPort: !Ref GRPCPort
CidrIp:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet2Cidr
Description: !Sub Inbound from Private Subnet2 to ${EnvironmentName} GRPC Port
EKSCluster:
Type: AWS::EKS::Cluster
Properties:
Name: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-${EKSClusterName}'
RoleArn:
"Fn::GetAtt": ["EKSIAMRole", "Arn"]
ResourcesVpcConfig:
SecurityGroupIds:
- !Ref ControlPlaneSecurityGroup
SubnetIds:
- !ImportValue
'Fn::Sub': '${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet1Id'
- !ImportValue
'Fn::Sub': '${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet2Id'
Version: '1.26'
EKSProfiles:
Type: AWS::EKS::Profile
Properties:
ClusterName: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-${EKSClusterName}'
ProfileName: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-EKS-Profiles'
PodExecutionRoleArn: !GetAtt
- EKSpodexecutionRole
- Arn
Selectors:
- Namespace: default
- Namespace: kube-system
- Namespace: temporal
- Namespace: external-secrets
Subnets:
- !ImportValue
'Fn::Sub': '${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet1Id'
- !ImportValue
'Fn::Sub': '${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet1Id'
DependsOn: EKSCluster
EFSSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: !Sub Security group for Elastic Search cluster of ${EnvironmentName} environment
GroupName: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-GroupNameEFS
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: !Ref EFSPort
ToPort: !Ref EFSPort
CidrIp:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet1Cidr
Description: !Sub Inbound from Private Subnet1 to ${EnvironmentName} efs filesystem mount
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: !Ref EFSPort
ToPort: !Ref EFSPort
CidrIp:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet2Cidr
Description: !Sub Inbound from Private Subnet2 to ${EnvironmentName} efs filesystem mount
Outputs:
EKSClusterEndpoint:
Description: 'EKS OIDC Connection URL'
Value:
"Fn::GetAtt": ["EKSCluster", "OpenIdConnectIssuerUrl"]
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}-EKSClusterEndpoint"
PodSecurityGroup:
Description: 'EKS Pod Security group'
Value:
Ref: PodSecurityGroup
Export:
Name: !Sub "${AWS::StackName}-PodSecurityGroup"
5. Specify Stack Details:
Enter a Stack name for your deployment.
Provide parameter values as needed.
Review and acknowledge the capabilities .
You can set additional stack options or tags if necessary.
6. Review and Create:
Review the stack details and configuration.
Click “Create stack” to initiate the deployment.
7. Monitor Stack Creation:
The CloudFormation stack creation process will begin.
Monitor the stack events in the AWS Management Console.
Summary :-
This AWS CloudFormation template serves as a blueprint for setting up an EKS cluster, enhancing operational efficiency and scalability for containerized applications.This template ensures that your EKS cluster is established in a secure and well-structured manner, allowing you to focus on deploying and managing containerized workloads without the hassle of manual setup and configuration. It’s a valuable resource for orchestrating robust and scalable Kubernetes-based applications in the AWS cloud environment.
#AWS #CloudFormation #AmazonEKS #Kubernetes #InfrastructureAsCode #DevOps #ContainerOrchestration #CloudComputing #Automation #ElasticKubernetesService
