Interconnecting AWS Realms: Orchestrating Database Connectivity Across AWS Accounts with CloudFormation

Introduction :-
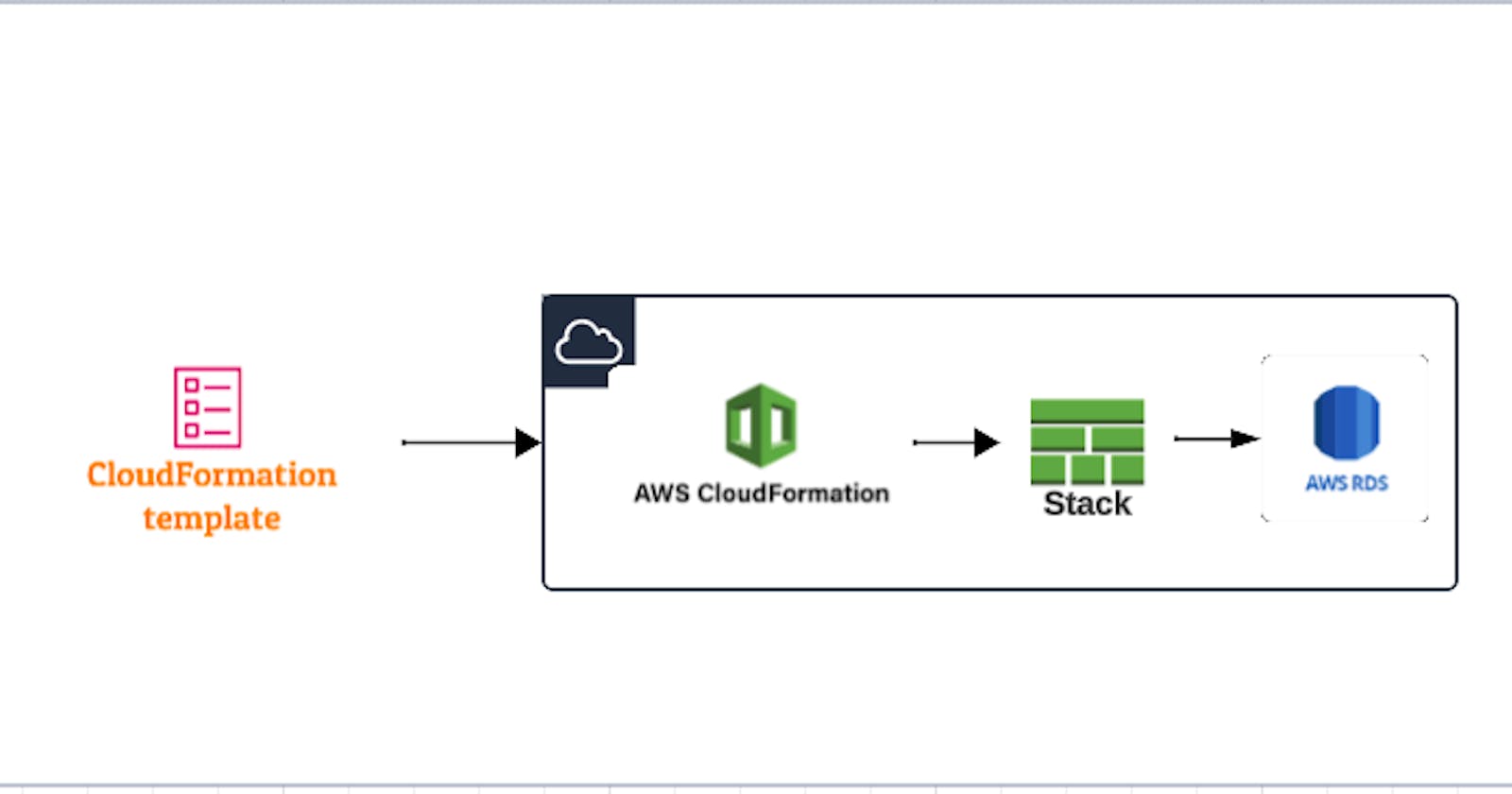
The provided #AWS CloudFormation template offers a comprehensive solution for establishing and maintaining database connectivity across different #AWS accounts or VPCs. In a dynamic and distributed AWS environment, the template automates the setup of essential resources to ensure seamless communication between #RDS (Relational Database Service) instances and an #Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) target group. This template addresses the challenge of handling evolving IP addresses and network configurations, making it an invaluable tool for system architects and administrators seeking a robust, automated solution.
#AWS CloudFormation template creates resources to facilitate database connectivity across #AWS accounts or VPCs. Here’s a breakdown of the template’s structure and purpose:
- Parameters: This section defines the input parameters that can be customized when creating the #CloudFormation stack. Users can specify values for these parameters during stack creation. The parameters in this template include:
EnvironmentName: A parameter for specifying the environment name (e.g., dev, staging, production).VPCid: A parameter to select the #VPC ID where the resources will be deployed. Users can choose from different #VPCs associated with different environments.SubnetsGroup: Allows users to choose the private subnets where private links and the #Lambda function will be deployed.TargetRoleARN: Specifies the #IAM Role ARN used to connect to the #VPC Endpoint service.RDSType: A parameter to select the type of #RDS (Relational Database Service) instance, with a default value of "db-cluster."RDSPOrt: The port number for the #RDS instance, with a default value of 1433.DBEndPoint: The endpoint of the #RDS, RDS Proxy, or Aurora Cluster.
2. Resources: This section defines the #AWS resources that will be created as part of the CloudFormation stack. Notable resources include:
LambdaPrivsRole: An #IAM role that allows the Lambda function to perform actions like creating and deleting network interfaces, interacting with #Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) resources, and managing CloudWatch Logs.LambdaSecurityGroup: An #AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) security group associated with the Lambda function.LambdaNLBUpdate: The #AWS Lambda function responsible for updating IP addresses within an #NLB target group based on RDS events.LambdaTriggerTopic: An #AWS Simple Notification Service (SNS) topic used to trigger the #Lambda function in response to RDS events.EventSubscription: An #AWS RDS Event Subscription that publishes RDS events to the SNS topic.NetworkLoadBalancer: An #AWS Elastic Load Balancer (NLB) for managing network traffic.NetworkLoadBalancerTargetGroup: A target group associated with the NLB.VPCEndpointService: An #AWS VPC Endpoint Service to allow external access to the NLB.
3. Outputs: This section provides outputs that allow you to access information about the resources created by the #CloudFormation stack. These outputs can include the #Lambda function name, the #SNS topic name, and other resource-related information.
Deployment Steps
Follow these steps to upload and create the CloudFormation stack using the AWS Management Console:
- Sign in to the #AWS Management Console: Log in to your AWS account if you haven’t already.
2. Navigate to #CloudFormation: Go to the #AWS CloudFormation service from the AWS Management Console.
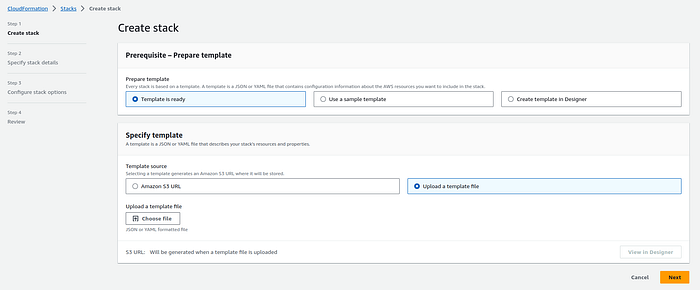
3. Click the “Create stack” button.
4. Upload the #CloudFormation template file (YAML).
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Description: "AWS CloudFormation Template for Database Connectivity"
Parameters:
EnvironmentName:
Description: Environment name (dev/staging/production)
Type: String
Default: dev
AllowedValues:
- dev
- staging
- production
ConstraintDescription: Specify either dev/staging/production
VPCid:
Description: VPC ID where resources will be deployed
Type: List<AWS::EC2::VPC::Id>
SubnetsGroup:
Description: Private subnets for resources
Type: List<AWS::EC2::Subnet::Id>
TargetRoleARN:
Description: IAM Role ARN for connecting to VPC Endpoint service
Type: String
MinLength: "1"
MaxLength: "256"
RDSType:
AllowedValues:
- db-cluster
- db-instance
Default: db-cluster
Type: String
RDSPOrt:
Type: Number
Default: "1433"
DBEndPoint:
Type: String
MinLength: "1"
MaxLength: "128"
Resources:
# Define AWS resources here
Outputs:
# Define outputs here
5. Specify Stack Details:
Enter a Stack name for your deployment.
Provide parameter values as needed.
Review and #acknowledge the capabilities .
You can set additional stack options or tags if necessary.
6. Review and Create:
Review the stack details and configuration.
Click “#Create stack” to initiate the deployment.
7. #Monitor Stack Creation:
The #CloudFormation stack creation process will begin.
Monitor the stack events in the #AWS Management Console.
Conclusion :-
In the world of #cloud computing, robust database connectivity is vital for ensuring the reliability and performance of applications. The #AWS CloudFormation template provided here simplifies the creation of essential resources, such as #Lambda functions, #IAM roles, security groups, and load balancers, to meet the unique demands of maintaining connectivity across different #AWS accounts or #VPCs. By leveraging this template, AWS users can enhance the #resilience and #scalability of their systems, facilitating the smooth operation of applications while reducing the administrative overhead associated with #IP address management. This template represents a powerful asset for modern cloud infrastructure deployments and underscores the #flexibility and automation capabilities of #AWS CloudFormation.