Streamlining Amazon Elasticsearch Service with AWS CloudFormation: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction :-
AWS CloudFormation is a powerful Infrastructure as Code (IAC) service that enables the automated provisioning and management of AWS resources through templates. These templates, written in either JSON or YAML, define the architecture and configuration of AWS resources, allowing for consistent and repeatable deployments.
The provided CloudFormation template is designed to deploy an Amazon Elasticsearch Service (Amazon ES) cluster, a popular managed search and analytics engine. Elasticsearch is known for its scalability and real-time search capabilities, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications. This template not only creates the Elasticsearch cluster but also configures associated networking resources, security groups, and advanced settings.
CloudFormation template is used to create an Amazon Elasticsearch Service (Amazon ES) cluster along with the necessary networking resources and security groups. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and settings in this template:
- Parameters:
These are values that can be passed in when creating the stack to customize the deployment.
Parameters include things like the environment name, domain name, instance type, Elasticsearch version, and more.
2. Conditions:
- These conditions determine whether certain resources should be created or configured based on parameter values. For example, the
HasSingleClusterInstancecondition checks if theClusterInstanceCountparameter is set to '1'.
3. Resources:
This section defines the AWS resources to be created as part of the stack deployment.
Key resources in this template include:
ElasticSearchServicelinkrole: An AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) service-linked role for Amazon ES.ElasticSearchSecurityGroup: An Amazon EC2 security group for the Elasticsearch cluster.ElasticSearchDomain: The Amazon ES domain itself, specifying various properties like access policies, instance configuration, and VPC options.
4. Outputs:
These are values that can be exported for use in other stacks or resources.
The main output here is the
ElasticSearchDomainEndpoint, which provides the endpoint for accessing the Elasticsearch cluster.
Deployment Steps
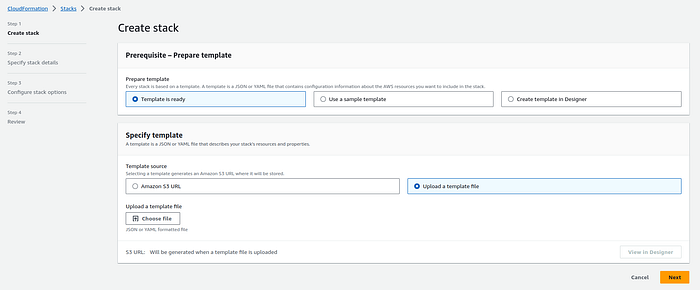
Follow these steps to upload and create the CloudFormation stack using the AWS Management Console:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console: Log in to your AWS account if you haven’t already.
2. Navigate to CloudFormation: Go to the AWS CloudFormation service from the AWS Management Console.
3. Click the “Create stack” button.
4. Upload the CloudFormation template file (YAML).
Yaml file :
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: 2010-09-09
Description: This stack deploys an elastic search cluster
Parameters:
EnvironmentName:
Description: Environment name for the application
Type: String
default: dev
DomainName:
Type: String
ElasticSearchAdminUserPassword:
NoEcho: true
Type: String
ElasticSearchAdminUserName:
Type: String
NetworkStackName:
Description: Name of an active CloudFormation stack of networking resources
Type: String
MinLength: 1
MaxLength: 255
AllowedPattern: "^[a-zA-Z][-a-zA-Z0-9]*$"
InstanceType:
Description: Instance Type for Elasticsearch Cluster
Type: String
InstanceVolumeSize:
Description: Instance Volume Size for Elasticsearch Cluster
Type: String
ElasticsearchVersion:
Description: Elasticsearch Version for Cluster
Type: String
ElasticsearchPort:
Description: Elasticsearch port
Default: 443
Type: Number
ClusterInstanceCount:
Description: 'The number of data nodes (instances) to use in the Amazon ES domain.'
Type: Number
Default: 1
DedicatedMasterCount:
Description: 'The number of dedicated master nodes (instances) to use in the Amazon ES domain (set to 0 to disable dedicated master nodes).'
Type: Number
Default: 0
DedicatedMasterType:
Description: 'The instance type for your dedicated master nodes.'
Type: 'String'
Conditions:
HasSingleClusterInstance: !Equals [!Ref ClusterInstanceCount, '1']
HasDedicatedMasterNodes: !Not [!Equals [!Ref DedicatedMasterCount, 0]]
Resources:
ElasticSearchServicelinkrole:
Type: AWS::IAM::ServiceLinkedRole
Properties:
AWSServiceName: es.amazonaws.com
ElasticSearchSecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: !Sub Security group for Elastic Search cluster of ${EnvironmentName} environment
GroupName: !Sub ${EnvironmentName}-${DomainName}-elasticsearch-sg
VpcId:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-VpcId
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: !Ref ElasticsearchPort
ToPort: !Ref ElasticsearchPort
SourceSecurityGroupId:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub SecurityGroupId
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: !Ref ElasticsearchPort
ToPort: !Ref ElasticsearchPort
CidrIp:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet1Cidr
Description: !Sub Inbound from Private Subnet1 to ${EnvironmentName} elasticsearch cluster
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: !Ref ElasticsearchPort
ToPort: !Ref ElasticsearchPort
CidrIp:
Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet2Cidr
Description: !Sub Inbound from Private Subnet2 to ${EnvironmentName} elasticsearch cluster
ElasticSearchDomain:
Type: AWS::Elasticsearch::Domain
Properties:
AccessPolicies:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
AWS: '*'
Action:
- 'es:*'
Resource:
- !Sub arn:aws:es:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:domain/${EnvironmentName}-${DomainName}-es/*
AdvancedSecurityOptions:
Enabled: true
InternalUserDatabaseEnabled: true
MasterUserOptions:
MasterUserName:username'
MasterUserPassword:password}}'
ElasticsearchClusterConfig:
InstanceType: !Ref InstanceType
InstanceCount: !Ref ClusterInstanceCount
ZoneAwarenessEnabled: !If [HasSingleClusterInstance, false, true]
DedicatedMasterCount: !If [HasDedicatedMasterNodes, !Ref DedicatedMasterCount, !Ref 'AWS::NoValue']
DedicatedMasterEnabled: !If [HasDedicatedMasterNodes, true, false]
DedicatedMasterType: !If [HasDedicatedMasterNodes, !Ref DedicatedMasterType, !Ref 'AWS::NoValue']
DomainEndpointOptions:
EnforceHTTPS: true
TLSSecurityPolicy: 'Policy-Min-TLS-1-2-2019-07'
DomainName: !Sub '${EnvironmentName}-${DomainName}-es'
EncryptionAtRestOptions:
Enabled: true
NodeToNodeEncryptionOptions:
Enabled: true
EBSOptions:
EBSEnabled: true
VolumeSize: !Ref InstanceVolumeSize
VolumeType: gp2
ElasticsearchVersion: !Ref ElasticsearchVersion
SnapshotOptions:
AutomatedSnapshotStartHour: 15
VPCOptions:
SubnetIds:
- Fn::ImportValue: !Sub ${NetworkStackName}-PrivateSubnet1Id
SecurityGroupIds:
- Fn::GetAtt:
- ElasticSearchSecurityGroup
- GroupId
DependsOn: ElasticSearchServicelinkrole
Outputs:
ElasticSearchDomainEndpoint:
Value: !GetAtt
- ElasticSearchDomain
- DomainEndpoint
Export:
Name: !Sub ${AWS::StackName}-ElasticSearchDomainEndpoint
5. Specify Stack Details:
Enter a Stack name for your deployment.
Provide parameter values as needed.
Review and acknowledge the capabilities .
You can set additional stack options or tags if necessary.
6. Review and Create:
Review the stack details and configuration.
Click “Create stack” to initiate the deployment.
7. Monitor Stack Creation:
The CloudFormation stack creation process will begin.
Monitor the stack events in the AWS Management Console.
Conclusion :-
In conclusion, the AWS CloudFormation template presented here streamlines the deployment of an Amazon Elasticsearch Service cluster, ensuring that the Elasticsearch environment is properly configured and secured. By utilizing parameters, conditions, and intrinsic functions, the template offers flexibility and customization options to adapt to various use cases and requirements.
#AWS #CloudFormation #AmazonElasticsearch #InfrastructureAsCode #DevOps #Elasticsearch #AWSManagement #CloudServices #Automation #TechGuide #AWSBestPractices #IaC #AWSArchitecture #DataManagement #AWSCommunity #CloudDevelopment #AWSDeployment #AWSResources #CloudComputing#MediumArticle
